WEB TUTORIAL - Group Theory
[Re2Cl8]2- Worked Example
| D4h | E | 2C4 (z) | C2 | 2C'2 | 2C''2 | i | 2S4 | 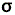 h h |
2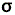 v v |
2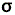 d d |
Rotations |
Functions |
Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1g | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | - | x2+y2, z2 | - |
| A2g | +1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | Rz | - | - |
| B1g | +1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | - | x2-y2 | - |
| B2g | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | - | xy | - |
| Eg | +2 | 0 | -2 | 0 | 0 | +2 | 0 | -2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | - |
| A1u | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | - | - | - |
| A2u | +1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | z | - | z3, z(x2+y2) |
| B1u | +1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | +1 | - | - | xyz |
| B2u | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | - | - | z(x2-y2) |
| Eu | +2 | 0 | -2 | 0 | 0 | -2 | 0 | +2 | 0 | 0 | (x, y) | - | (xz2, yz2) (xy2, x2y), (x3, y3) |
h = 16
Now we have all of the required parts we simply put then together into the Reduction Formula one row at a time. This calculation will be quite long, but it is important that you are able to compute a reduction of this size.
It is worth doing this on a piece of paper rather than trying in your head before checking your answers!